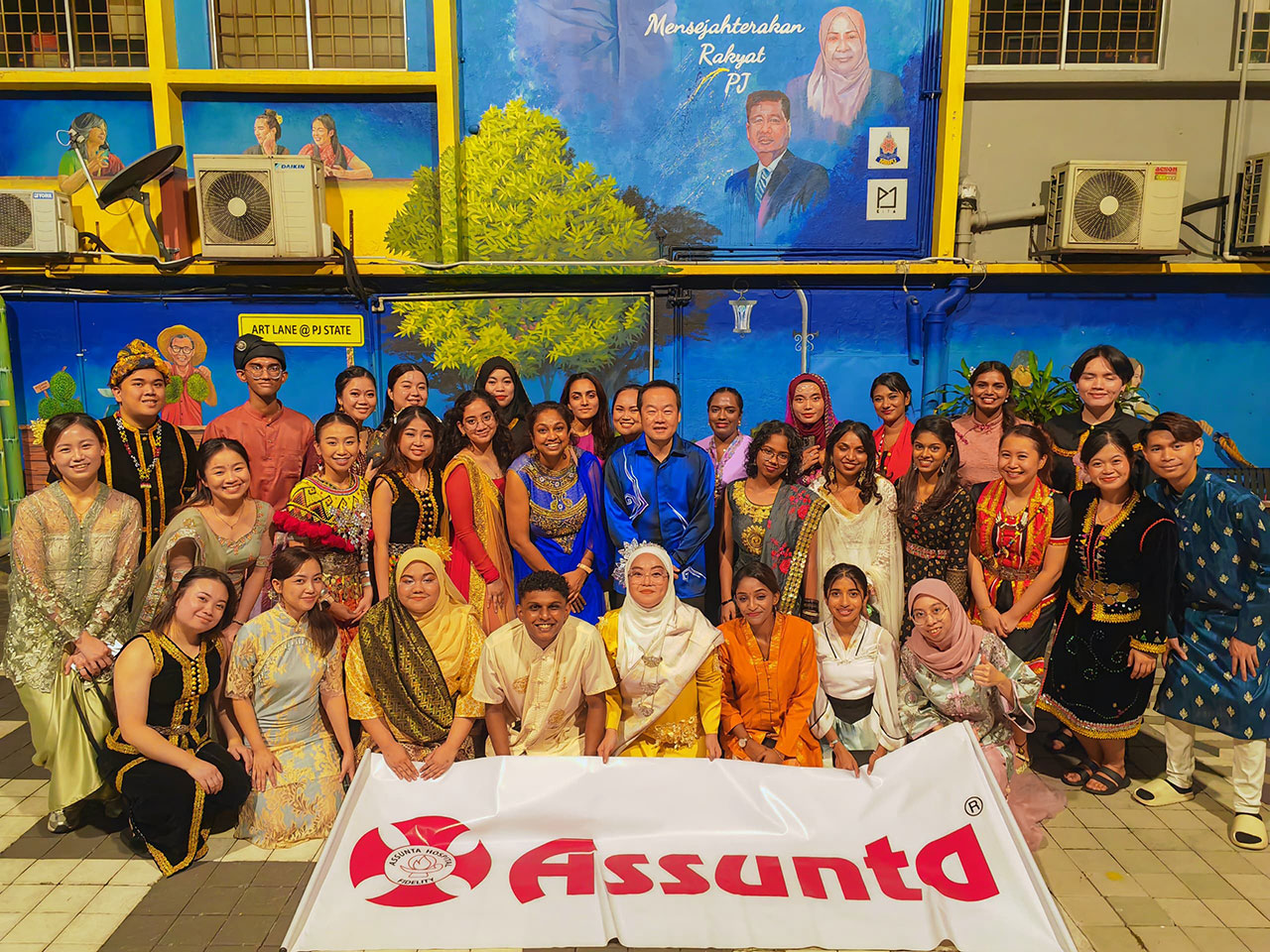
Protect Your Baby And Care For Yourself: Pay Attention to Thyroid Health During Pregnancy
- Updated on: June 12, 2024

Related Articles

Health Articles
Exploring The Intersection of ENT Health and Diving Medicine: A Guide for Healthcare Professionals
Read More »
29/05/2024